

Running a convenience store can be a lucrative business venture, but it requires careful planning to ensure financial success. Convenience store financials form the foundation of any successful business operation, and building a good financial model is crucial to achieving profitability. This convenience store financial model template can help you create a comprehensive plan that accounts for all expenses, from inventory and salaries to utilities and rent, and provides financial projections for your business. In this blog post, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to build a financial model for a convenience store business plan financials.
Convenience Store Financial Projections play a vital role in the smooth running of the business. Revenue & Sales Forecast is an essential part of it. This model provides a financial plan for the convenience store. It states the revenue figures that the store is expected to generate over a given period. The forecast model's success depends on the accuracy of the underlying assumptions.
The forecast period should start from the store's Launh date and should cover the Sales Ramp-Up Time, Walk-In Traffic & Growth Assumptions, Customer and Purchases Assumptions, Sales Seasonality, etc.
The launch date of your convenience store is one of the most important decisions you'll make. Your launch date sets the stage for your entire business, affecting everything from your financial projections to your customer base. It's critical to choose a launch date that maximizes your chances of success.
When choosing your launch date, consider factors like the seasonality of your business, local events, and the availability of your products. You'll also need to account for the time it takes to prepare your store for opening, including stocking shelves, training employees, and marketing your business.
By carefully selecting your launch date and preparing your store for opening, you'll be well positioned for success in the highly competitive convenience store industry. Good luck!
Forecasting sales is an essential aspect of convenience store financial analysis. To accurately predict future sales, it is important to consider the ramp-up time to sales plateau. Ramp-up time is the length of time it takes for a business to reach a steady level of sales, or plateau, after opening.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
Different factors, such as location, competition, and marketing strategies, can affect the ramp-up time to sales plateau. As such, the convenience store financial plan should include a realistic estimation of ramp-up time.
What is the sales ramp-up period for your business? This can be determined by analyzing industry data and incorporating this into the convenience store financial forecast. Depending on the location and competition, the ramp-up period can vary from several months to over a year.
To ensure convenience store financial feasibility, a proper understanding of ramp-up time and accurate financial projections is necessary. With these insights, financial management becomes more feasible concerning the overall success of the business.
After the ramp-up period, the average walk-in daily traffic of visitors in our convenience store has been consistent. On Mondays, the average walk-in traffic is 150 customers, while on Tuesdays, it's 160 customers. Wednesdays tend to be quiet, with 140 customers walking in, and so on for the rest of the weekdays.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
This information is crucial for developing a convenience store financial model template that will help us predict future performance, inform growth decisions, and guide our convenience store business plan financials. With this consistent traffic, we can estimate gross sales and calculate expenses to determine our profitability.
Based on historical data and market trends, we forecast a growth factor of 2% per year for the next five years. Therefore, we expect to see an increase in daily traffic every year across all weekdays, providing growth potential for the convenience store.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
Tips & Tricks:
The consistent traffic inputs are just one of the many inputs necessary for a comprehensive Convenience store financial feasibility, analysis, projections, plan, statement, forecast, management that enable our convenience store to make informed decisions, predict sales and expenses, and plan for growth.
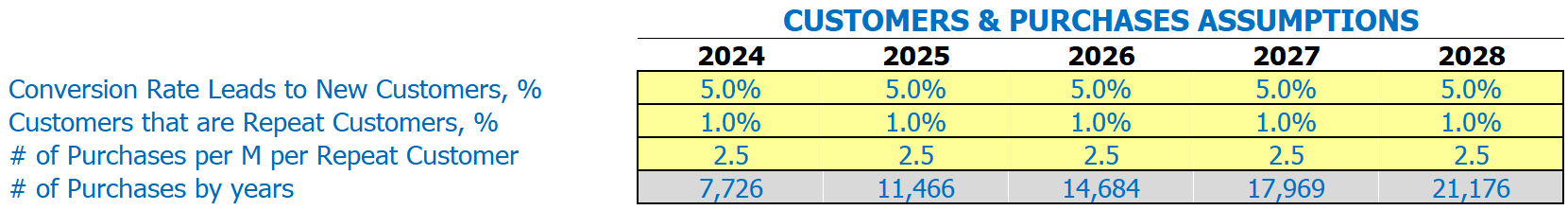
Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
When starting a Convenience Store, it is important to know the number of visitors you receive and how many of those will become repeat customers. To start your financial model, you need to estimate your conversion rate, which is typically between 20% to 40%. This means that for every 10 visitors, two to four of them will make a purchase.
To estimate the number of repeat customers, you need to track them on a monthly basis, and you can start by assuming that 20% to 40% of your customers are repeat customers. Once you have a clear data set of your customer base, you can start to make sales projections based on their buying habits.
Assuming that the average repeat customer will make two purchases per month, you can use this information to estimate your sales for your Convenience Store. This information will allow you to make important financial projections for your business.
Understanding the percentage of visitors turning into regular customers and the amount of purchasing that each customer makes per month are essential inputs in building your Convenience Store’s financial model. It’s an important part of analyzing the financial feasibility and management of the business, which makes the Convenience store financial analysis, financial performance, financial plan, and financial statement an essential part of business operations.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
When it comes to the convenience store business plan financials, having a clear understanding of your sales mix is crucial. This means knowing what products your store is selling and how they contribute to your revenue.
It's helpful to categorize your products into different product categories such as snacks, beverages, hygiene products, etc. This makes entering sales mix assumptions on the product category level much easier for understanding.
For example, let's say your store sells five different product categories: chips, candy, soda, energy drinks, and gum. You can enter the sales mix in percentage for each of the five years forecast per product category.
Our Convenience store business plan financials heavily rely on various inputs to accurately project financial performance. One of the most important inputs is the average selling amount, or ASA, of each product category. Our store offers a range of products, such as snacks, drinks, cigarettes, and personal care items, each belonging to a specific category.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
Instead of estimating ASA for each product separately, we enter assumptions on a category level. For instance, let's assume the snacks category includes chips, candy bars, and nuts. We can estimate an ASA for the snacks category as a whole, based on the sales mix of each product within the category.
Let's say that in the first year, chips represent 50% of all snack sales, candy bars are 30%, and nuts are 20%. We can estimate the ASA for each product, for example, chips sell for $1.50 on average, candy bars for $2, and nuts for $3. Based on these numbers, the ASA for the snack category in the first year is calculated as:
Snacks ASA = (50% x $1.50) + (30% x $2) + (20% x $3) = $1.70
We repeat this process for every product category and every year of our convenience store financial projections. The ASA is then used to calculate the Average Ticket Size (ATS), which measures the average amount spent per customer per visit.
Using the sales mix and ASA of each category, the model calculates the ATS as follows:
ATS = (Sales from Category 1 x ASA Category 1 + Sales from Category 2 x ASA Category 2 + . + Sales from Category N x ASA Category N)/ Total Number of Transactions
Seasonality greatly impacts a convenience store's financial performance.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
Therefore, it is critical to explain these assumptions in detail. For example, during the summertime, sales typically increase in categories such as cold drinks, ice cream, and sunscreen. Meanwhile, wintertime can increase sales in categories such as coffee, packaged food, and tobacco.
As far as how seasonal factors should look across the calendar year, it is dependent on the needs of the convenience store's specific customer base. However, it is crucial to maintain a balanced revenue stream throughout the year, with proper forecasting and anticipated inventory levels based on the established seasonal factors. For example, if the store has an average daily sales figure of $2,000, it is possible to anticipate a 20% deviation in July and August, with an increase in sales to $2,400. Conversely, in January and February, winter weather and holidays may cause a deviation of -15% in sales, with an average daily sales figure of $1,700.

In order to properly plan the financials for a convenience store, it is crucial to make an Operational Expenses Forecast. This Forecast includes Cost of Goods Sold by Products %, Employee Salaries and Wages, Rent, Lease or Mortgage Payment, Utilities, and Other Running Costs.
| Expense Type | Amount (per month) USD |
|---|---|
| Cost of Goods Sold by Products % | $4,000 - $6,000 |
| Employee Salaries and Wages | $3,500 - $5,000 |
| Rent, Lease or Mortgage Payment | $3,000 - $5,000 |
| Utilities | $800 - $1,500 |
| Other Running Costs | $1,000 - $1,500 |
| Total | $13,300 - $19,500 |
Properly forecasting the operational expenses for a convenience store is an important aspect of the financial plan for the business. By understanding these expenses and implementing proper financial management, a convenience store can maintain healthy financial performance.
The Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is the sum of all the direct expenses required to manufacture or sell a particular item. In a convenience store business, COGS includes the cost of goods sold such as snacks, beverages, tobacco products, and lottery tickets. Since COGS is a significant expense of a convenience store, accurate estimation of COGS is crucial for creating a sound Convenience Store Financial Plan.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
Convenience Store Financial Projections involve estimating the amount of revenue and expenses for a specific period. COGS is one of the major expenses of a convenience store. Accurate estimation of COGS depends on several factors such as product mix, customer preferences, competition, and seasonality.
For example, if a convenience store owner is selling chips, then the COGS would include the direct cost of acquiring the chips (e.g., wholesale price), plus any variable expenses related to the purchase of the chips (e.g., transportation costs, taxes). The percentage of COGS for the chips category would depend on the gross profit margin that the owner wants to achieve.
By regularly monitoring COGS, convenience store owners can make better financial decisions and enhance their Convenience Store Financial Performance. COGS is part of a convenience store's Financial Statement, which includes revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities. Accurate estimation of COGS is crucial for convenience store financial Management and Feasibility.
When creating a convenience store financial plan, it's essential to consider your employee salaries and wages. Here are some of the assumptions to keep in mind:

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
By taking into consideration these factors, you'll be able to develop a strong financial plan for your convenience store, ensuring your staff is well-compensated and your business runs smoothly.
When creating a convenience store financial plan, it is important to take into account the rent, lease, or mortgage payment assumptions. These payments are a significant expense and can greatly impact the store's financial performance.
Rent: This is a fixed amount paid for the use of a property, typically on a monthly basis. For example, if a convenience store rents a space for $2,500 per month, this expense will be included in the financial statements each month.
Lease: This is a contract outlining the terms of renting a property, usually for a fixed period such as 5 years. The lease payment will typically be lower than rent payments on a month-to-month basis, but will be a longer-term commitment. For example, a convenience store may sign a lease for a space at $2,000 per month for 5 years.
Mortgage Payment: This is a payment made to a lender when purchasing a property. The payment includes the principal and interest on the loan, as well as property taxes and insurance. For example, a convenience store may purchase a property for $500,000 with a mortgage payment of $3,000 per month.
When creating a convenience store financial plan, one crucial aspect to consider is utilities. Utilities expenses can vary depending on the location and size of the store, which is why making proper assumptions is essential.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
Assuming that a convenience store will consume electricity and water, it is essential to prepare for the costs adequately. The electricity rates will depend on the state and region in which the store is located. Checking the rates and assuming a consumption level is the first step to estimating the expense. Water expenses will again depend on location and usage.
One example of a utilities assumption that must be made is the cost of lighting for the store. Here, the convenience store business plan financials will vary depending on the size of the store, number of bulbs, and type of bulbs used. Using more energy-efficient bulbs can significantly reduce the electricity expenses.
Having a clear understanding of utilities expenses and making proper assumptions is a vital part of creating a successful financial plan for a convenience store. It helps to ensure that the expense does not become a liability, and the store does not face any unforeseen difficulties.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
When building a financial model for your convenience store, it is important to include all potential costs. Besides rent, utilities, and employee wages, there are other operating expenses to consider that might seem like minor expenses, but they can add up quickly.
Insurance: As a convenience store owner, you will need to purchase insurance to cover potential damages or injuries caused by accidents, theft, or vandalism.
Supplies: You will also need to buy supplies such as bags, shopping carts, cleaning products, and office supplies that contribute to your store’s daily operations.
Maintenance and Repair: It's important to prepare for regular maintenance expenses like lawn care, HVAC system maintenance and repairs, and exterior repairs such as fixing damage caused by storms.
Marketing and Advertising: To promote your convenience store and attract customers, you will need to invest in advertising and marketing activities. There are various advertising platforms like local newspapers, radio, online advertising, and even on social media. You might also need to invest in promo displays or discounts to attract and retain customers.
The aforementioned miscellaneous expenses are often overlooked but they are important since they contribute to your convenience store financial projections. It is important to consider all costs and factor them into your financial model so that your convenience store business plan financials will appear as true and accurate as possible.
When creating a financial plan for your convenience store business, forecasting is a crucial step in determining its financial viability. A financial forecast provides an estimate of future financial performance, often presented as a Profit and Loss Statement or Sources and Uses Report. By utilizing a Convenience Store Financial Model Template and conducting a thorough Convenience Store Financial Analysis, you can accurately project your business's financial outcomes and identify areas for improvement.
Once we have created the convenience store financial projections, it is time to analyse the Convenience store financial performance in terms of profitability. We can start by examining the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement from the revenues down to the net profit. This will give us an idea of how much money we can make after accounting for all the expenses.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
By examining the P&L statement, we can calculate important metrics such as gross profit and EBITDA margin. Gross profit is the amount of money you have left over after accounting for all the costs of goods sold, while EBITDA margin measures earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortisation.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
Using these metrics, you can determine the convenience store financial feasibility, and convenience store financial model template that will work best for you. By understanding all the factors that contribute to profitability, you can create a convenience store financial plan that is both realistic and profitable.
With a sound convenience store financial management approach, you can monitor your profitability over time and make adjustments as necessary to ensure continued success.
The sources and uses of funds statement within the financial model in Excel for Convenience Store provides users an organized summary of where capital will come from Sources and how this capital will be spent in the Uses.

Source: Convenience Store Financial Model
It is important for the total amounts of sources and uses to be equal to each other. The sources and uses statement is particularly critical when the company is considering or going through a recapitalization, restructuring, or mergers & acquisitions (M&A) procedure.
Use a financial model to plan your convenience store's success financially. By creating a comprehensive financial model for your convenience store, you can plan its operations and estimate its expenses and revenues. When building this model, it's important to include all of your expenses, including rent, utilities, labor costs, and inventory, as well as your expected profit margins. Use these projections to tweak your business plan and make it financially feasible, and use the insights derived from your financial analysis to make sound business decisions. A financial model is a critical tool for all convenience store owners, as it helps you stay on track with your financial goals and keeps your business in line with your financial projections, ensuring that your store remains profitable and sustainable over time.